Heat Conduction in One Dimension
Heat Conduction in One Dimension: Overview
This topic covers concepts such as Heat Transfer, Thermal Conduction, The Steady State Heat Flow, Heat Flow and Area of Cross Section, Heat Flow and Temperature Gradient, Coefficient of Thermal Conductivity, etc.
Important Questions on Heat Conduction in One Dimension
of heat is conducted through wall of thickness in . Temperature difference between the two sides of the wall is . The thermal conductivity of the material of the wall is (in ) . Write the value of .
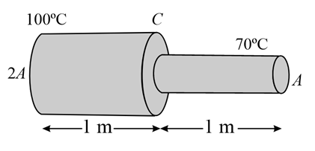
A metal rod of length has cross sectional areas and as shown in the figure. The ends are maintained at temperatures and . The temperature at middle point is___.
The end of a rod of length is maintained at and the end at . What is the temperature (in ) at a distance of from the end ?
Two heater coils separately take and to boil a certain amount of water. If both the coils are connected in series, the time taken to boil water is
Cloudy nights are usually warmer than clear ones, because clouds
SI unit of temperature gradient is
Which one of the following is not the example of the athermanous medium.
Which one of the following is not the example of the diathermanous medium.
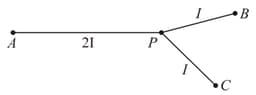
Three rods (lengths made of the same material and having the same area of cross-section are joined as shown in figure. The end points and are maintained at constant temperatures and respectively. Assuming that there is no loss of heat from the surface of the rods, find the temperature that the junction ultimately reaches.
Two rods of the same length and diameter having thermal conductivities and are joined in parallel. The equivalent thermal conductivity of the combination is
A long metallic bar is carrying heat from one of its ends to the other end under a steady state. The variation of temperature along the length of the bar from its hot end is best described by which of the following figure?
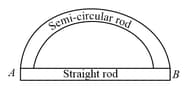
Two rods (one semi-circular and other straight) of the same material and of same cross-sectional area are joined as shown in the diagram. The points and are maintained at different temperatures. The ratio of the heat transferred through a cross-section of a semi-circular rod to the heat transferred through a cross-section of the straight rod in a given time is
If the power consumption is ,
The thermal conductivity of air is:
The lengths and radii of two rods made of same material are in the ratios and , respectively. If the temperature difference between the ends for the two rods be the same, then in steady state, the amount of heat flowing per second through them will be in the ratio,
A partition wall has two layers of different materials and in contact with each other. They have the same thickness but the thermal conductivity of layer is twice that of . At steady state, if the temperature difference across the layer is , then the corresponding temperature difference across the layer is
The thermal conductivity of air is:
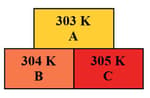
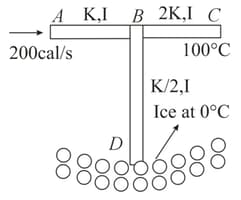
Three rods and of same length and cross-sectional area are arranged as shown. The end is immersed in ice whose mass is and is at . The end is maintained at . Heat is supplied at constant rate of . Thermal conductivities of and are and , respectively. Time after which whole ice will melt is
In the given diagram, the possible direction of heat energy transformation is
Explain athermanous medium with an example.